
There may be no other signs or symptoms at first. The most common sign of childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a painless lump or swelling in soft tissues of the body.Ī sarcoma may appear as a painless lump under the skin, often on an arm, a leg, or the trunk.
Having AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) and Epstein-Barr virus infection at the same time. Other risk factors include the following: Risk factors for childhood soft tissue sarcoma include having the following inherited disorders: Talk with your child’s doctor if you think your child may be at risk. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Having certain diseases and inherited disorders can increase the risk of childhood soft tissue sarcoma.Īnything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Soft tissue sarcoma in children may respond differently to treatment, and may have a better prognosis than soft tissue sarcoma in adults. Soft tissue sarcoma occurs in children and adults. In children, the tumors form most often in the arms, legs, or trunk (chest and abdomen). Soft tissue sarcoma may be found anywhere in the body. Synovial tissues (tissues around joints). Tendons (bands of tissue that connect muscles to bones). Soft tissues of the body connect, support, and surround other body parts and organs. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.Ĭhildhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body. There are many different types of soft tissue sarcomas. If tests show there may be a soft tissue sarcoma, a biopsy is done. Diagnostic tests are used to detect (find) and diagnose childhood soft tissue sarcoma. The most common sign of childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a painless lump or swelling in soft tissues of the body. Having certain diseases and inherited disorders can increase the risk of childhood soft tissue sarcoma. Soft tissue sarcoma occurs in children and adults. Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body. Tumour recurrence: occasionally the parotid tumour may recur at any time after the surgery. In 1% of cases there is a permanent weakness of the face following this sort of surgery for benign tumours. In most cases the nerve works normally after the surgery However, occasionally when the tumour has been very close to the nerve, a temporary weakness of the face can occur that can last a few weeks. This makes the muscles of the face move and if damaged during the surgery there may be a weakness of the face (facial palsy). Facial weakness: There is a very important nerve, the facial nerve, which passes right through the parotid gland. This can usually be treated easily by the application of a roll-on antiperspirant. This is because the nerve supply to the parotid gland can regrow to supply the sweat glands of the overlying skin, instead of the parotid. Freys syndrome: Some patients find that after this surgery their cheek can become red, flushed and sweaty whilst eating. #MOVABLE LUMP ON JAW JOINT SKIN#
Numbness of the face and ear: The skin of the side of the face will be numb for some weeks after the operation, and often you can expect your ear lobe to be numb permanently. Seroma: This is build up of bodily fluid occurring at the site of surgery. Your surgeon will recommend a bland diet for several days following surgery to minimise salivary collection. If the saliva collects under the skin, it can be removed with a needle. Salivary collection: The cut surface of the parotid gland leaks a little saliva, which may collect under the skin or drain through the skin. This occurs in about 5% of patients and it is sometimes necessary to return to the operating theatre and remove the clot and replace the drain. 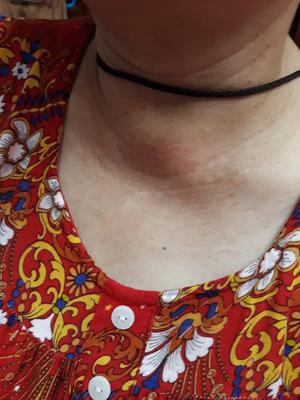
Blood clot: A blood clot (haematoma) may collect under the skin. Rarely there pus may collect under the skin (abscess), which is best treated be surgically draining the pus. Infection: Occasionally, the wound may become swollen, red, tender and warm to touch (cellulitis).






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
